An Animal That Eats Other Animals Like a Jellyfish
An Animal That Eats Other Animals Like a Jellyfish
Jellyfish are bonny, transparent, small, oval-like bounding main creatures that have lived for millions of years. In actuality, their entire lifecycle revolves around h2o, and this is practically truthful because jellyfish are nigh 95 percent water. They have tentacles used for hunting and are known for their stinging ability – a defense mechanism. Jellyfish take neither blood, center, os, brain, or other organs. They only consist of three layers: the outer layer known as the epidermis, a thick elastic and leased substance called mesoglea, and an inner layer called gastrodermis.
The Background on Jellyfish
Jellyfish are simple invertebrates that belong to the phylum Cnidaria, including sea anemones, Alcyonacea, and Coral. Incidentally, the body parts of a jellyfish radiate from the key centrality, which allows them to recognize and respond to food and danger from all directions. A jellyfish tin sting with tentacles, particularly when it senses danger. The severity of stings varies; nonetheless, most jellyfish stings crusade merely slight discomfort to humans. They take tiny stinging cells on their tentacles that stun or paralyze their prey before eating it. Their bong-shaped body has an opening, which serves as a mouth and anus. Jellyfish eat and dispose of the waste from this opening, and they can live for up to three to half-dozen months and grow up to 7 anxiety. In as much as they take all these fantastic attributes, several other ocean creatures consume jellyfish daily.
What Eats Jellyfish?

Grey triggerfish, ocean sunfish, seabirds, turtles, whale sharks, venereal, and whales swallow jellyfish naturally. However, the main predators of jellyfish are usually other dissimilar types of jellyfish.
The jellyfish is a pelagic fish that lives in the open sea from the torrid zone to the Arctic Ocean. Although it can move its umbrella rhythmically, it practically lives at the mercy of sea currents. The jellyfish'southward body exhibits radial symmetry and is divided into three master parts: an umbrella, the arm of the mouth (around the rima oris), and a stinging tentacle. They are blest with internal cavities where digestion takes place – amazingly, this cavity has a single opening that serves both the oral cavity and anus.
Jellyfish Predators: Ocean Sunfish
Sunfish are predators who eat various foods simply their favorite delicacy is jellyfish. Since jellyfish are almost entirely water and depression in calories and nutrients, fish as large as sunfish eat a pregnant amount of them to back up their weight. These jellyfish predators are e'er on a hunting spree for these bounding main creatures because of their surprisingly high growth rate and weight which adds to their nutritional value.
Jellyfish Predators: Seabirds
Sea birds eat jellyfish by pecking their inner tissues to avoid their tentacles. Since jellyfish are 95 percent h2o, predators have to eat them in big amounts to get higher dietary nourishment.
Jellyfish Predators: Turtles
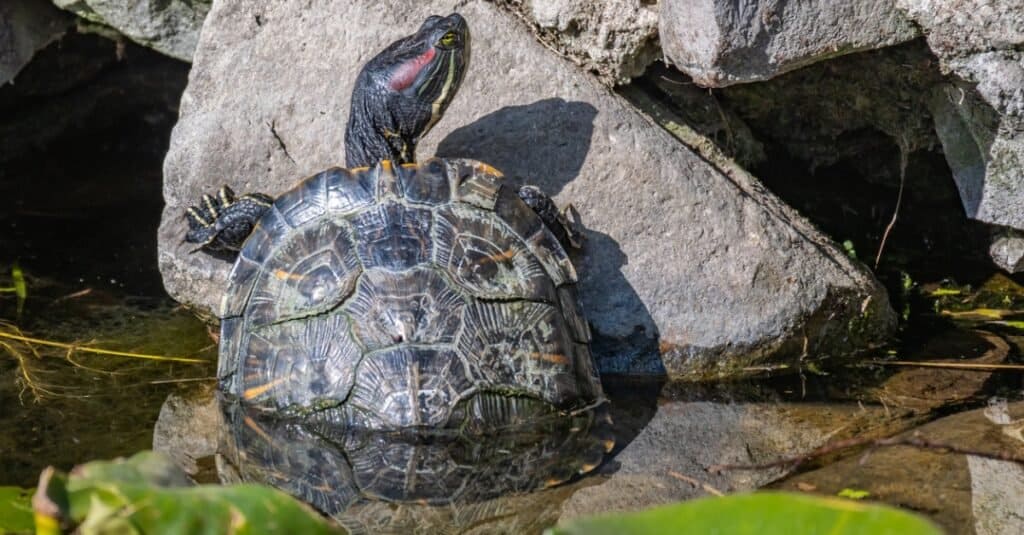


A jellyfish has long trailing tentacles total of stinging cells to ward off predators. All the same, the turtle even so feeds on it without getting stung. Specific evolutionary adaptations/defense mechanisms have given turtles an edge over jellyfish's stings. Interestingly, turtles have thick skin, especially around their beaks – protecting them from the excruciating pains of jelly stings. They also possess papillae that line their oral cavity, which helps them get a grip on their favorite meal and prevent prey from slipping.
Jellyfish Predators: Crabs
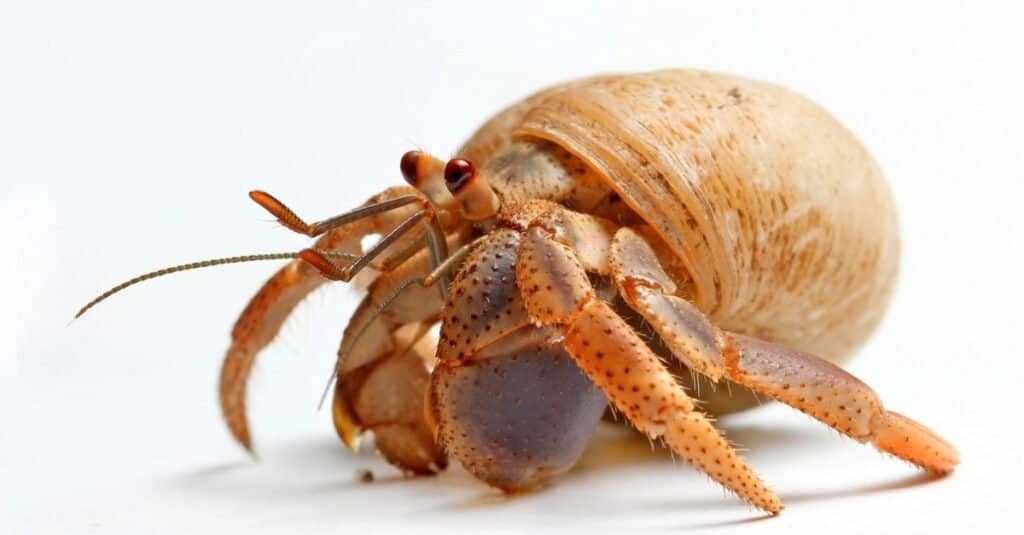


Because crabs live in the ocean depths, they often have difficulty accessing several jellyfish. They by and large feed on dying jellyfish. Surprisingly, the stinging cells of a jellyfish are unlikely to penetrate or interfere with the hard crab shell or mouthpiece.
Jellyfish are magnificent water creatures to behold. The lack of essential body organs common to other animals would go out one wondering how they survive and alive their daily lives. Intriguingly, we have answers to some of these questions. And so, let's dive further as nosotros unravel the surviving tactics of these water creatures and their habitat below:
What Do Jellyfish Eat?


Jellyfish are primarily carnivores. Astoundingly, when food is abundant in the bounding main, they grow exponentially in size and brood in large numbers. However, nutrient shortages ever have a fashion of diminishing their sizes and procreating abilities. These gelatinous animals accept elementary anatomy, only they are however very effective. Jellyfish mainly eat zooplankton, minor crustaceans, and in some cases, minor fish and other breeds of jellyfish.
How Jellyfish Reproduce
Male person and female jellyfish reproduce by releasing sperm and eggs into the h2o (sexual reproduction). After fertilization, they develop larvae that produce new jellyfish and polyps that settle on the seabed. New free-living jellyfish can grow from these polyps through asexual reproduction.
How Jellyfish Defend Themselves
Jellyfish tentacles with stinging cells serve as a defense and a powerful weapon for communicable prey. When in close range with their target, the nematocysts (poisonous cells) present in the tentacles release the harpoons and filaments, releasing toxic substances that paralyze their prey. Their oral artillery help to catch and swallow the captured bounding main creatures.
Are Jellyfish Poisonous?
The complete lack of encephalon makes jellyfish sting at the slightest sense of danger. Jellyfish stings can be painful and sometimes dangerous to humans. Nevertheless, jellyfish do not knowingly set on humans. For every one centimeter of its tentacles, a jellyfish has 3 one thousand thousand stinging cells. When a jellyfish's stinging cells come in close contact with the human skin, it releases poison. Some possible effects of jellyfish poison include:
- Skin swelling or redness around the afflicted area
- Severe pains all over
- Feel difficulty in breathing, swallowing, and even talking
- Profuse sweating accompanied by shivering
- Experiencing headache, vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea
- Irregular pulse
Do Jellyfish Eat Other Fish?
Mostly, all jellyfish tend to exist passive feeders, which implies that they feed on whatever comes their mode as they are tossed from one identify to another by ocean currents. Jellyfish practically eat whatsoever passes in the water and can fit well in their rima oris, including krill, shrimp, and small fish.
More from A-Z Animals
An Animal That Eats Other Animals Like a Jellyfish
Source: https://a-z-animals.com/blog/jellyfish-predators-what-eats-jellyfish/



Komentar
Posting Komentar